Technology Trends Shaping the Business Landscape of 2025
Related Articles: Technology Trends Shaping the Business Landscape of 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Technology Trends Shaping the Business Landscape of 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Technology Trends Shaping the Business Landscape of 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Technology Trends Shaping the Business Landscape of 2025
- 3.1 1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 3.2 2. Internet of Things (IoT)
- 3.3 3. Cloud Computing
- 3.4 4. Cybersecurity
- 3.5 5. Blockchain Technology
- 3.6 6. Edge Computing
- 3.7 7. Extended Reality (XR)
- 3.8 8. Quantum Computing
- 3.9 Related Searches
- 3.10 FAQs
- 3.11 Tips
- 3.12 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Technology Trends Shaping the Business Landscape of 2025

The rapid evolution of technology continues to reshape the business landscape, creating opportunities and challenges for organizations of all sizes. As we approach 2025, certain trends are poised to dominate the technological landscape, influencing how businesses operate, compete, and interact with their customers. Understanding and adapting to these trends will be crucial for success in the years to come.
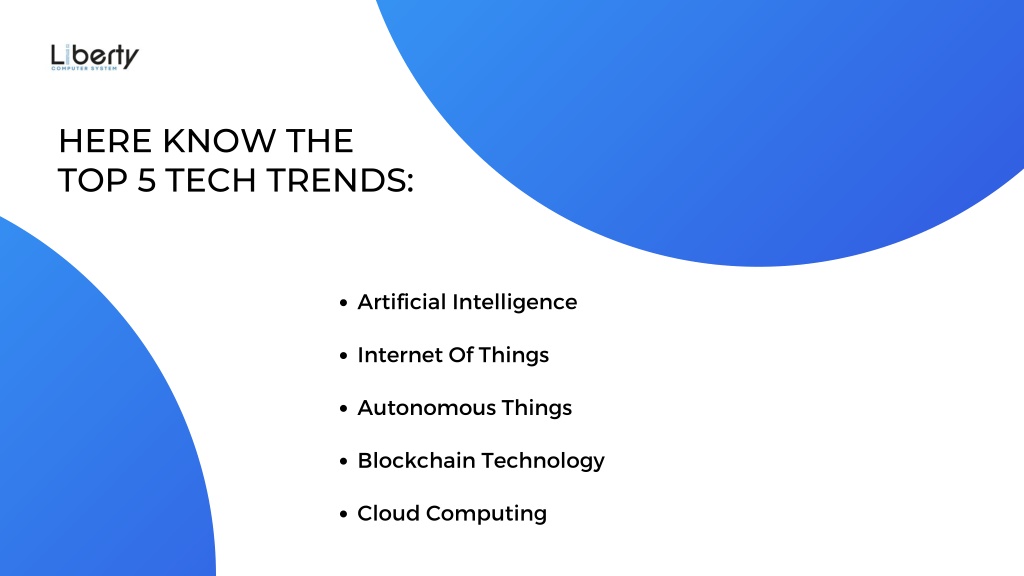
Here are eight key technology trends that will shape the business world in 2025:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
-
AI and ML are no longer futuristic concepts; they are becoming increasingly integrated into business operations. AI-powered tools are being used for tasks like data analysis, automation, customer service, and even decision-making.
-
Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: AI automates repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic work.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide personalized and efficient customer support.
- Data-Driven Insights: ML algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and generate insights that can inform business strategy.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can predict future trends and outcomes, allowing businesses to make proactive decisions.
-
Examples:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze sensor data from machinery to predict potential failures, allowing for preventative maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, protecting businesses from financial losses.
- Personalized Marketing: AI can analyze customer data to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with individual preferences.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
-
The IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data. This network is expanding rapidly, with billions of devices expected to be connected by 2025.
-
Benefits:
- Real-Time Data Collection: IoT devices provide continuous streams of data that can be used to optimize operations and make better decisions.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: IoT sensors can monitor and control processes in real-time, leading to increased efficiency and reduced waste.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: IoT devices can personalize services and provide customers with real-time information and support.
-
Examples:
- Smart Factories: IoT sensors monitor production processes, optimizing resource utilization and reducing downtime.
- Connected Healthcare: Wearable devices track patient health metrics, providing real-time insights to healthcare providers.
- Smart Cities: IoT networks manage traffic flow, optimize energy consumption, and improve public safety.
3. Cloud Computing
-
Cloud computing has become the backbone of modern businesses, offering scalable and flexible computing resources on demand.
-
Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Cloud computing eliminates the need for expensive hardware investments, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use.
- Increased Agility: Businesses can scale their computing resources up or down quickly to meet changing demands.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud-based tools facilitate collaboration among teams, regardless of their location.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, offering a more secure environment than many on-premises solutions.
-
Examples:
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Cloud-based applications like Salesforce and Microsoft 365 offer a wide range of business functionalities.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Cloud providers like AWS and Azure offer virtual servers, storage, and networking resources on demand.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Cloud platforms like Heroku and Google App Engine provide development environments and tools for building and deploying applications.
4. Cybersecurity
-
Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as businesses rely more heavily on digital technologies.
-
Benefits:
- Protection of Sensitive Data: Cybersecurity measures protect businesses from data breaches and other cyberattacks.
- Compliance with Regulations: Businesses must comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Business Continuity: Cybersecurity safeguards ensure that businesses can continue operating in the event of a cyberattack.
-
Examples:
- Multi-factor Authentication: Requires users to provide multiple forms of identification to access sensitive systems.
- Endpoint Security: Protects devices from malware and other threats.
- Data Encryption: Protects data from unauthorized access, even if it is stolen.
5. Blockchain Technology
-
Blockchain is a decentralized and secure ledger that records transactions across a network of computers.
-
Benefits:
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain transactions are publicly auditable, promoting transparency and trust.
- Improved Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes it resistant to tampering and fraud.
- Reduced Costs: Blockchain can streamline processes and eliminate intermediaries, reducing transaction costs.
-
Examples:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track products throughout the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and transparency.
- Financial Services: Blockchain can facilitate faster and more secure financial transactions.
- Digital Identity: Blockchain can be used to create secure and verifiable digital identities.
6. Edge Computing
-
Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance.
-
Benefits:
- Reduced Latency: Processing data at the edge reduces the time it takes for information to travel to a central server.
- Improved Performance: Edge computing can handle real-time applications and data-intensive tasks more efficiently.
- Increased Security: Data processed at the edge is less vulnerable to security breaches.
-
Examples:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing enables self-driving cars to process sensor data in real-time, making critical decisions.
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing allows factories to monitor and control production processes in real-time, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Smart Homes: Edge computing enables smart home devices to respond to user requests and environmental changes in real-time.
7. Extended Reality (XR)
-
XR encompasses technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR).
-
Benefits:
- Enhanced Training and Education: XR technologies provide immersive and interactive training experiences.
- Improved Customer Engagement: XR can create engaging and interactive customer experiences.
- Product Design and Development: XR allows businesses to visualize and test product designs before they are built.
-
Examples:
- VR Training Simulators: VR simulations provide realistic training environments for employees in industries like healthcare and manufacturing.
- AR Shopping Apps: AR apps allow customers to visualize products in their own homes before purchasing them.
- MR Collaboration Tools: MR tools allow teams to collaborate on projects in a shared virtual space, regardless of their physical location.
8. Quantum Computing
-
Quantum computing utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems that are intractable for traditional computers.
-
Benefits:
- Drug Discovery: Quantum computers can simulate complex molecular interactions, accelerating drug discovery and development.
- Materials Science: Quantum computing can help design new materials with improved properties.
- Financial Modeling: Quantum computers can analyze financial markets and make more accurate predictions.
-
Examples:
- Quantum Machine Learning: Quantum computers can accelerate machine learning algorithms, leading to more powerful AI applications.
- Quantum Cryptography: Quantum computing can be used to develop unbreakable encryption methods.
- Quantum Simulation: Quantum computers can simulate complex physical systems, leading to breakthroughs in fields like physics and chemistry.
Related Searches
1. Future of Work: The technological trends discussed above will significantly impact the future of work. AI and automation will automate many tasks, leading to a shift towards higher-skilled jobs that require creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. Businesses will need to invest in upskilling and reskilling their workforce to adapt to these changes.
2. Digital Transformation: Digital transformation refers to the process of integrating digital technologies into all aspects of a business. The trends discussed above are driving digital transformation, enabling businesses to operate more efficiently, innovate faster, and deliver better customer experiences.
3. Business Analytics: AI and ML are driving advancements in business analytics, allowing businesses to extract valuable insights from data. This data-driven approach helps businesses make better decisions, optimize operations, and improve customer satisfaction.
4. Customer Experience (CX): Technology trends like AI, IoT, and XR are transforming the customer experience. Businesses are using these technologies to personalize interactions, provide seamless experiences, and build stronger customer relationships.
5. Cybersecurity Threats: The increasing reliance on digital technologies has also led to a rise in cybersecurity threats. Businesses need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect their data, systems, and reputation.
6. Blockchain Applications: Blockchain technology is finding applications in various industries, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. Businesses are exploring how blockchain can improve transparency, security, and efficiency in their operations.
7. Edge Computing Use Cases: Edge computing is finding use cases in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. It enables businesses to process data in real-time, improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
8. XR in Business: XR technologies are being adopted by businesses across industries for training, marketing, and product development. These technologies offer immersive and interactive experiences that can enhance engagement and productivity.
FAQs
1. How can businesses prepare for these technology trends?
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest technological advancements and their potential impact on your industry.
- Invest in Skills Development: Upskill and reskill your workforce to adapt to the changing job market.
- Embrace Experimentation: Experiment with new technologies to identify opportunities and challenges.
- Partner with Technology Providers: Collaborate with technology providers to leverage their expertise and resources.
2. What are the potential risks of these technology trends?
- Job Displacement: Automation may lead to job losses in certain sectors.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of data-driven technologies raises concerns about privacy and data security.
- Ethical Considerations: AI and other technologies raise ethical questions about bias, accountability, and the potential for misuse.
3. How can businesses mitigate these risks?
- Invest in Workforce Training: Prepare employees for the jobs of the future through upskilling and reskilling programs.
- Prioritize Data Privacy: Implement robust data privacy and security measures to protect customer data.
- Develop Ethical Guidelines: Establish clear ethical guidelines for the use of AI and other technologies.
4. How will these technology trends impact different industries?
- Healthcare: AI and IoT will revolutionize healthcare by enabling personalized treatments, remote monitoring, and improved diagnostics.
- Manufacturing: Smart factories and edge computing will optimize production processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
- Retail: AI-powered personalization and AR/VR experiences will transform the customer experience in retail.
- Finance: Blockchain technology will streamline financial transactions, improve security, and reduce costs.
Tips
- Focus on Customer Needs: Use technology to improve the customer experience and build stronger relationships.
- Embrace Data-Driven Decision-Making: Leverage data analytics to make informed decisions and optimize operations.
- Prioritize Cybersecurity: Invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect your data and systems.
- Foster Innovation: Encourage a culture of innovation and experimentation to stay ahead of the curve.
- Collaborate with Technology Partners: Partner with technology providers to access expertise and resources.
Conclusion
The technology trends discussed above will continue to shape the business landscape in the years to come. Businesses that embrace these trends and adapt to the changing environment will be well-positioned for success. By staying informed, investing in skills development, and fostering a culture of innovation, businesses can leverage technology to drive growth, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Technology Trends Shaping the Business Landscape of 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!