Shaping the Future: Trends in Globalization 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Trends in Globalization 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Trends in Globalization 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shaping the Future: Trends in Globalization 2025

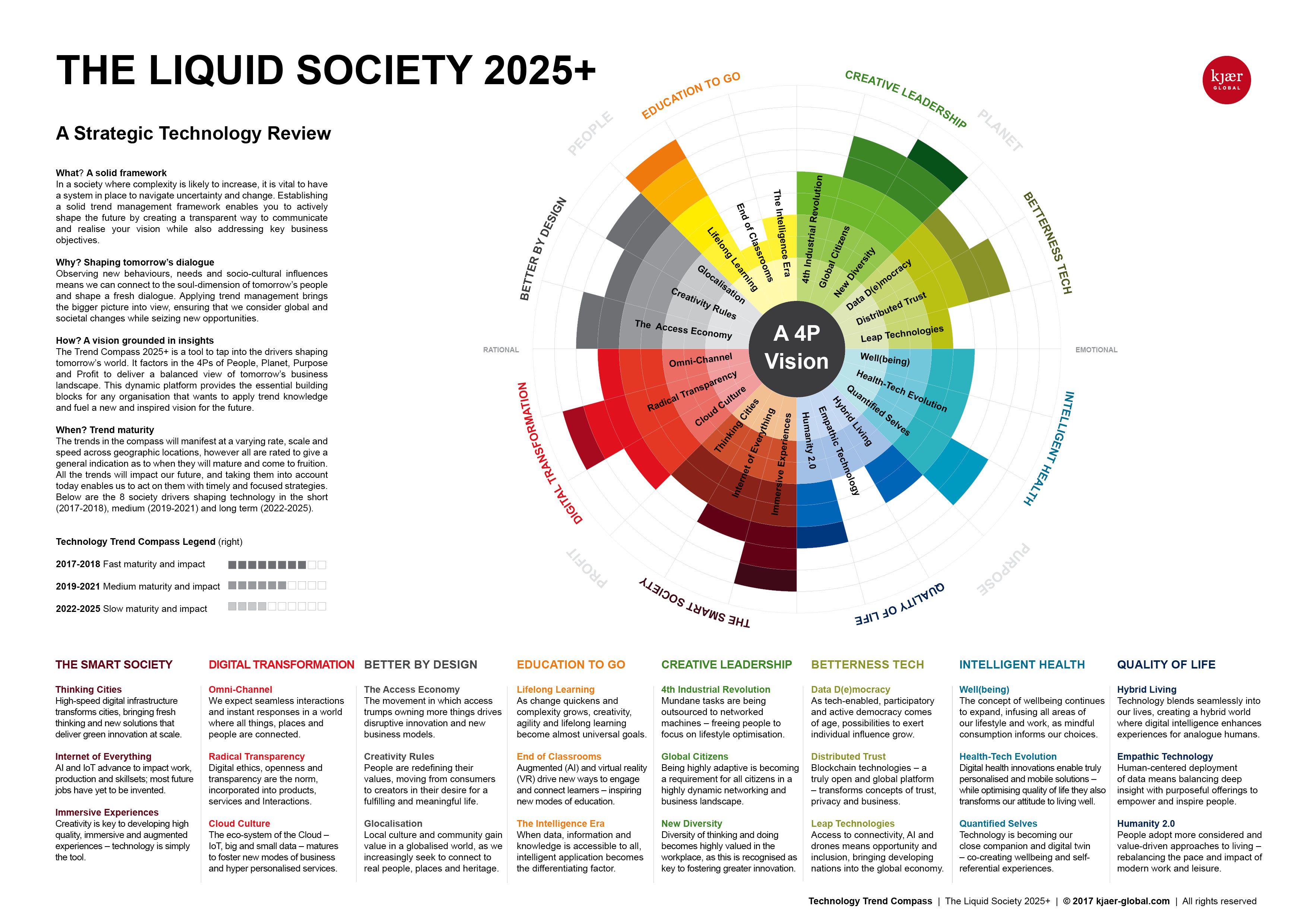
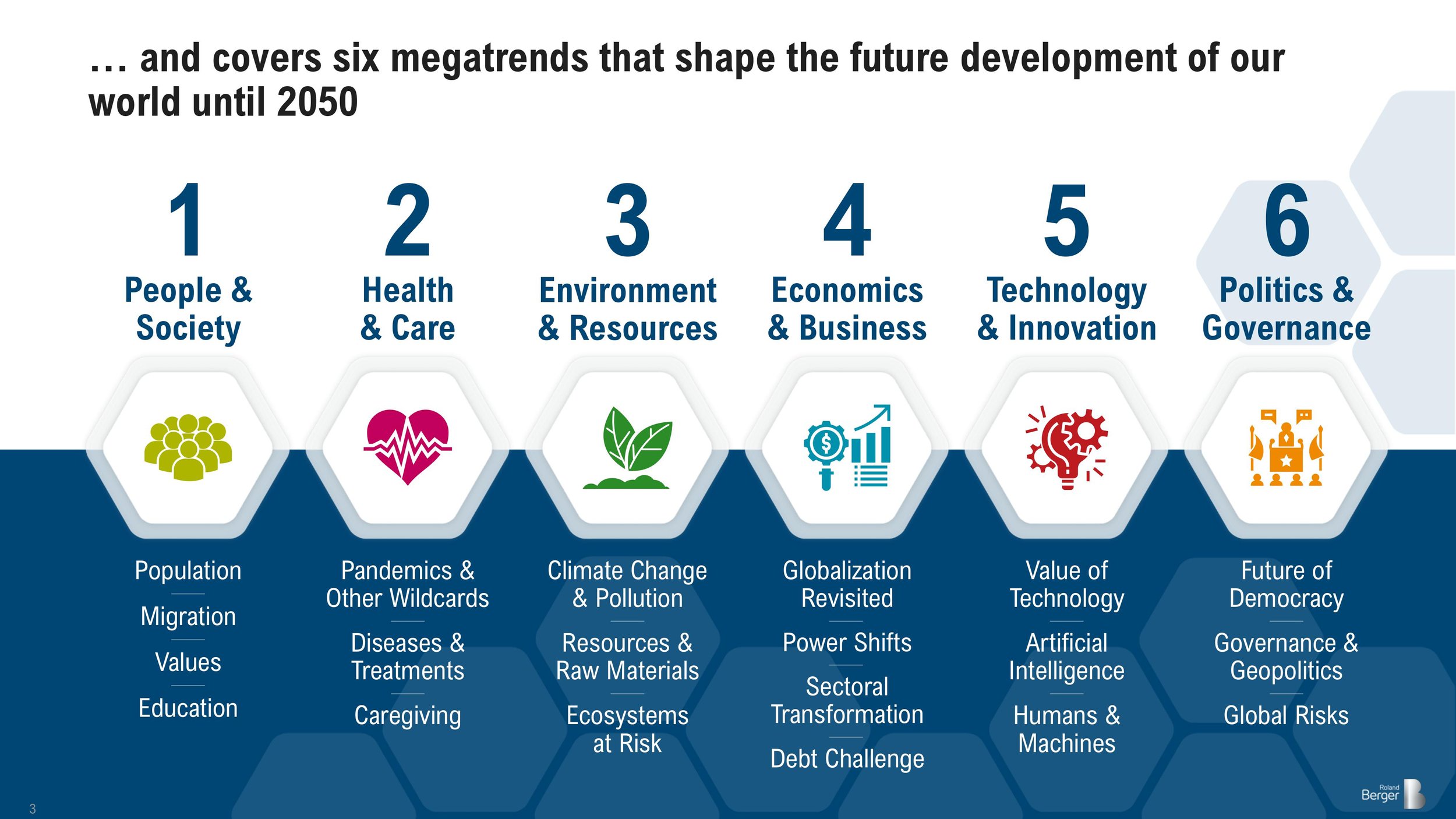
The world is in constant flux, and the forces of globalization are a driving factor in this dynamic evolution. As we stand on the cusp of 2025, it is essential to understand the trends shaping this interconnected world and their potential implications. Trends in globalization 2025 will be defined by a complex interplay of technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and evolving societal values.
1. Technological Advancements: Catalysts for Globalization
Technological innovation has always been a potent driver of globalization, and this trend will only intensify in the coming years.
a. Digital Infrastructure: The expansion of high-speed internet access, coupled with the proliferation of mobile devices, will bridge geographical divides and facilitate seamless communication and collaboration. This will foster a more interconnected global marketplace, enabling businesses to operate across borders with greater ease.
b. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is poised to revolutionize various industries, from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and education. Its ability to automate tasks, analyze data, and generate insights will lead to increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation, fostering a more integrated global economy.
c. Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s decentralized and transparent nature will revolutionize financial transactions, supply chains, and data management. Its potential to streamline cross-border payments, enhance security, and foster trust will contribute to a more efficient and interconnected global economy.
2. Geopolitical Shifts: Reshaping the Global Landscape
The global landscape is undergoing significant geopolitical shifts, with implications for the future of globalization.
a. The Rise of Asia: The economic rise of Asia, particularly China and India, is reshaping the global balance of power. This shift is leading to increased trade and investment flows between Asia and the rest of the world, fostering new economic partnerships and alliances.
b. The Multipolar World: The traditional bipolar world order is giving way to a multipolar world with multiple centers of power. This will lead to a more complex and dynamic global landscape, requiring greater cooperation and diplomacy to manage geopolitical challenges.
c. Regional Integration: Regional trade blocs and alliances are gaining prominence, facilitating trade and investment within specific geographical areas. This trend is creating new opportunities for regional economic growth and development, while also potentially contributing to fragmentation of the global economy.
3. Evolving Societal Values: Shaping the Global Agenda
Societal values are evolving rapidly, impacting the direction of globalization.
a. Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: Growing awareness of climate change and environmental degradation is driving a global movement towards sustainable practices. This is leading to the adoption of green technologies, renewable energy sources, and responsible consumption patterns, influencing global trade and investment decisions.
b. Social Justice and Equality: Increasing awareness of social inequalities and injustices is prompting calls for greater social responsibility and inclusivity. This is driving initiatives to promote fair trade practices, ethical sourcing, and equitable distribution of wealth, impacting the global economic landscape.
c. Digital Inclusion: The digital divide is a significant challenge, with limited access to technology hindering participation in the global economy. Initiatives to bridge this gap, such as promoting digital literacy and affordable internet access, are crucial for achieving a more equitable and inclusive globalization.
4. Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Future of Globalization
Trends in globalization 2025 present both challenges and opportunities.
a. Inequality and Social Disruption: While globalization can create economic opportunities, it can also exacerbate income inequality and lead to social unrest. Addressing this challenge requires policies that promote inclusive growth and provide social safety nets for those who are left behind.
b. Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Wars: The rise of nationalism and protectionism can lead to trade wars and geopolitical tensions, hindering global economic integration. Diplomacy and international cooperation are essential to manage these challenges and foster a more stable and prosperous global economy.
c. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: The increasing interconnectedness of the global economy raises concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy. Robust safeguards are needed to protect sensitive information and ensure the security of critical infrastructure.
d. Environmental Sustainability: Globalization can contribute to environmental degradation if not managed responsibly. Sustainable practices, responsible resource management, and international cooperation are crucial to mitigate the environmental impact of globalization.
Related Searches:
1. Impact of Globalization on Developing Countries:
Globalization has a complex and multifaceted impact on developing countries. While it can foster economic growth and create new opportunities, it can also exacerbate inequality, lead to exploitation, and undermine local economies.
a. Economic Growth and Development: Globalization can provide developing countries with access to new markets, technologies, and investments, contributing to economic growth and development.
b. Inequality and Exploitation: Globalization can also lead to increased inequality, as multinational corporations may exploit cheap labor and resources in developing countries, benefiting from lax regulations and weak labor protections.
c. Dependence on Developed Economies: Globalization can create a dependence on developed economies, making developing countries vulnerable to economic shocks and fluctuations in the global market.
2. Globalization and the Environment:
Globalization has both positive and negative implications for the environment. While it can facilitate the sharing of knowledge and technologies for environmental protection, it can also contribute to environmental degradation through increased consumption, pollution, and resource depletion.
a. Environmental Degradation: Increased production and consumption driven by globalization can lead to increased pollution, deforestation, and resource depletion, impacting the environment globally.
b. Environmental Cooperation: Globalization can facilitate international cooperation on environmental issues, enabling countries to share knowledge, technologies, and best practices for environmental protection.
c. Sustainable Development: Globalization can promote sustainable development by encouraging the adoption of green technologies, renewable energy sources, and responsible consumption patterns.
3. Globalization and Culture:
Globalization has a profound impact on culture, leading to increased cultural exchange, convergence, and hybridization. This can lead to both positive and negative consequences, with the potential to enrich cultural diversity while also posing threats to traditional values and identities.
a. Cultural Exchange and Convergence: Globalization facilitates the exchange of ideas, customs, and traditions across borders, leading to cultural convergence and hybridization.
b. Cultural Homogenization: Globalization can also lead to cultural homogenization, as dominant cultures and products spread globally, potentially eroding local traditions and identities.
c. Cultural Preservation: Globalization can also play a role in cultural preservation, by promoting the appreciation and understanding of diverse cultures and traditions.
4. Globalization and Labor Markets:
Globalization has a significant impact on labor markets, leading to both opportunities and challenges. It can create new jobs and opportunities for workers, but it can also lead to job displacement, wage stagnation, and increased competition for jobs.
a. Job Creation and Opportunities: Globalization can create new jobs and opportunities in sectors such as manufacturing, services, and technology, benefiting workers in both developed and developing countries.
b. Job Displacement and Wage Stagnation: Globalization can also lead to job displacement, as companies relocate operations to countries with lower labor costs, potentially affecting workers in developed economies.
c. Labor Standards and Rights: Globalization can raise concerns about labor standards and rights, as companies may exploit workers in countries with weak regulations and inadequate labor protections.
5. Globalization and Trade:
Globalization has led to a dramatic increase in international trade, with goods and services flowing freely across borders. This has created opportunities for economic growth and development, but it has also raised concerns about fair trade practices, protectionism, and the impact on local economies.
a. Free Trade and Economic Growth: Globalization has facilitated free trade, leading to increased economic growth and development by allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods and services they are most efficient at.
b. Protectionism and Trade Wars: The rise of nationalism and protectionism can lead to trade wars, hindering economic integration and growth.
c. Fair Trade Practices: Globalization has also raised concerns about fair trade practices, as multinational corporations may exploit workers and resources in developing countries.
6. Globalization and Technology:
Technological advancements are driving globalization, facilitating communication, transportation, and trade across borders. However, these advancements also raise concerns about digital inequality, cybersecurity, and the potential for technology to exacerbate existing inequalities.
a. Digital Connectivity: Technological advancements have facilitated digital connectivity, enabling businesses and individuals to communicate and collaborate across borders.
b. Digital Divide: However, access to technology is unevenly distributed, creating a digital divide that can exacerbate existing inequalities.
c. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: The increasing interconnectedness of the global economy raises concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy, as sensitive information is shared across borders.
7. Globalization and Politics:
Globalization has a profound impact on politics, leading to increased interdependence, the rise of global governance institutions, and the emergence of new political actors.
a. Interdependence and Global Governance: Globalization has increased interdependence between countries, leading to the emergence of global governance institutions to address issues that transcend national boundaries.
b. Non-State Actors: Globalization has also given rise to new political actors, such as multinational corporations, non-governmental organizations, and social movements, which can influence global policy decisions.
c. Nationalism and Populism: The rise of nationalism and populism can be seen as a backlash against globalization, as some individuals and groups feel that globalization has eroded their national identity and economic security.
8. Globalization and Health:
Globalization has significant implications for global health, facilitating the spread of infectious diseases, but also providing opportunities for collaboration and innovation in healthcare.
a. Global Health Threats: Globalization has facilitated the rapid spread of infectious diseases, such as pandemics, as people and goods travel across borders.
b. Global Health Collaboration: Globalization has also fostered international cooperation in healthcare, enabling countries to share knowledge, technologies, and resources to address global health challenges.
c. Healthcare Innovation: Globalization can also drive innovation in healthcare, as researchers and companies collaborate to develop new treatments and technologies.
FAQs by Trends in Globalization 2025
1. What are the potential benefits of globalization?
Globalization can bring numerous benefits, including:
- Economic Growth: Globalization facilitates trade, investment, and technological transfer, contributing to economic growth and development.
- Increased Consumer Choice: Globalization provides consumers with access to a wider variety of goods and services at competitive prices.
- Job Creation: Globalization can create new jobs and opportunities in various sectors, particularly in developing countries.
- Cultural Exchange: Globalization fosters cultural exchange and understanding, promoting tolerance and diversity.
- Technological Advancement: Globalization facilitates the sharing of knowledge and technologies, driving innovation and progress.
2. What are the potential drawbacks of globalization?
Globalization can also have negative consequences, such as:
- Income Inequality: Globalization can exacerbate income inequality, as multinational corporations may exploit cheap labor and resources in developing countries.
- Job Displacement: Globalization can lead to job displacement, as companies relocate operations to countries with lower labor costs.
- Environmental Degradation: Globalization can contribute to environmental degradation through increased production and consumption.
- Cultural Homogenization: Globalization can lead to cultural homogenization, as dominant cultures and products spread globally, potentially eroding local traditions and identities.
- Loss of National Sovereignty: Globalization can erode national sovereignty, as countries become more interconnected and subject to international agreements and regulations.
3. How can we mitigate the negative impacts of globalization?
Mitigating the negative impacts of globalization requires a multifaceted approach, including:
- Promoting Fair Trade Practices: Implementing fair trade practices that ensure equitable compensation for workers and producers in developing countries.
- Investing in Education and Skills Development: Providing workers with the skills and knowledge they need to compete in a globalized economy.
- Strengthening Labor Standards: Enforcing strong labor standards and protecting workers’ rights in all countries.
- Promoting Sustainable Development: Implementing policies that promote sustainable development, such as reducing pollution and conserving natural resources.
- Supporting International Cooperation: Fostering international cooperation to address global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and inequality.
4. What role will technology play in shaping the future of globalization?
Technology will play a crucial role in shaping the future of globalization, enabling greater interconnectedness, facilitating trade and investment, and driving innovation. However, it is essential to ensure that technological advancements are used responsibly and equitably to mitigate potential negative impacts.
5. What are the key challenges facing globalization in the future?
Globalization faces several challenges in the future, including:
- Geopolitical Tensions: The rise of nationalism and protectionism can lead to trade wars and geopolitical tensions, hindering global economic integration.
- Inequality and Social Disruption: Globalization can exacerbate income inequality and lead to social unrest if not managed effectively.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: The increasing interconnectedness of the global economy raises concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy.
- Environmental Sustainability: Globalization can contribute to environmental degradation if not managed responsibly.
Tips by Trends in Globalization 2025
1. Embrace Technological Advancements: Businesses and individuals must embrace technological advancements to stay competitive in a globalized economy. This includes investing in digital infrastructure, adopting new technologies, and developing digital literacy skills.
2. Foster International Collaboration: Collaboration across borders is essential for addressing global challenges and seizing opportunities. This includes promoting international trade, investment, and knowledge sharing.
3. Prioritize Sustainability: Businesses and individuals must prioritize sustainability in all aspects of their operations, from sourcing materials to reducing their environmental footprint.
4. Promote Social Responsibility: Businesses and individuals should strive to promote social responsibility by ensuring fair labor practices, ethical sourcing, and equitable distribution of wealth.
5. Stay Informed and Adaptable: The global landscape is constantly evolving, so it is essential to stay informed about emerging trends and adapt strategies accordingly.
Conclusion by Trends in Globalization 2025
Trends in globalization 2025 will be shaped by a complex interplay of technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and evolving societal values. This dynamic environment presents both challenges and opportunities. By embracing technological innovation, fostering international collaboration, prioritizing sustainability, promoting social responsibility, and staying informed and adaptable, individuals and businesses can navigate the future of globalization and contribute to a more interconnected, equitable, and sustainable world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Trends in Globalization 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!