Shaping the Future: Pharmaceutical Industry Trends 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Pharmaceutical Industry Trends 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Pharmaceutical Industry Trends 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shaping the Future: Pharmaceutical Industry Trends 2025
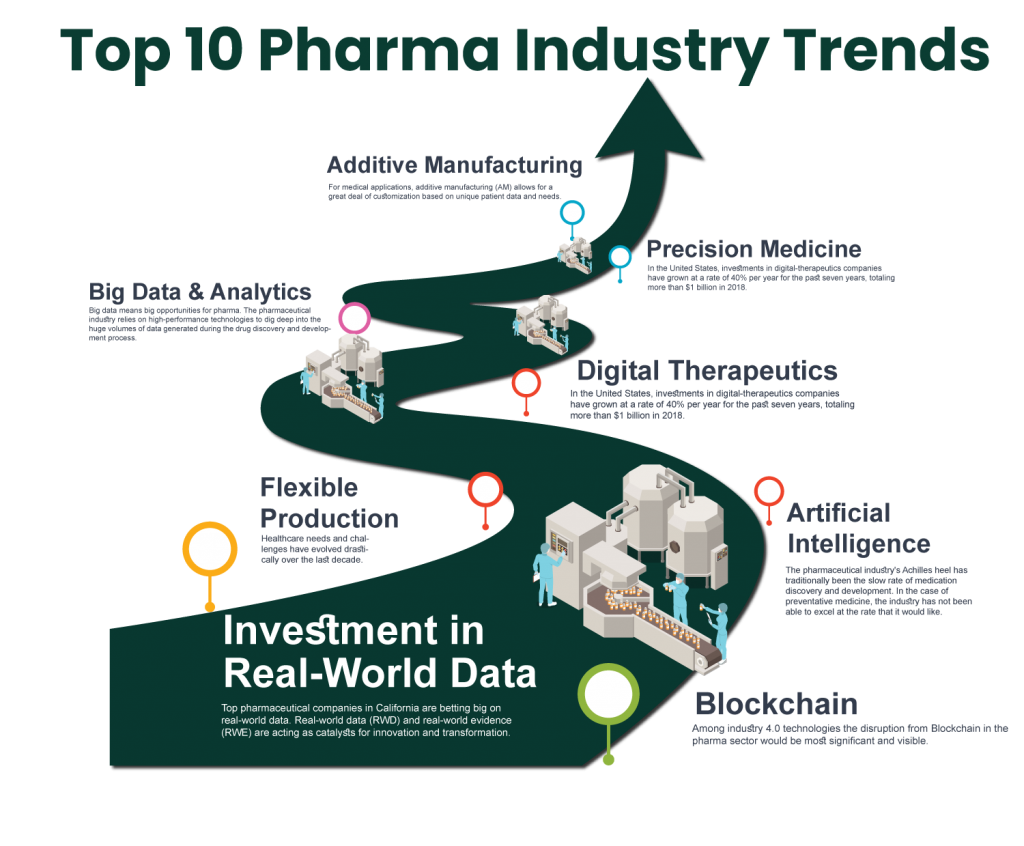
The pharmaceutical industry is a dynamic and constantly evolving landscape, driven by scientific breakthroughs, technological advancements, and shifting global health priorities. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the industry’s trajectory, impacting everything from drug discovery and development to patient care and market access. This comprehensive analysis delves into these trends, examining their implications and highlighting the opportunities they present.
1. Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments to Individual Needs
Personalized medicine is rapidly transforming healthcare, moving away from one-size-fits-all approaches to therapies that are customized to individual patients’ genetic makeup, lifestyle, and disease characteristics. This trend is fueled by advances in genomics, proteomics, and other "omics" technologies, enabling the identification of specific biomarkers and genetic variations that influence drug response and disease susceptibility.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine:
- Enhanced Treatment Effectiveness: By tailoring treatments to individual patients, personalized medicine can significantly improve treatment effectiveness, leading to better outcomes and reduced side effects.
- Improved Patient Safety: By identifying patients at risk of adverse drug reactions, personalized medicine can enhance patient safety and minimize the potential for drug-related complications.
- Cost Reduction: By optimizing treatment regimens and reducing the need for trial-and-error approaches, personalized medicine can contribute to cost savings in the long run.
Examples of Personalized Medicine in Action:
- Cancer Treatment: Genomic profiling of tumors allows for the development of targeted therapies that specifically attack the cancer cells, reducing the impact on healthy tissues.
- Cardiovascular Disease Management: Genetic testing can identify individuals at high risk of heart disease, enabling proactive lifestyle modifications and preventative measures.
- Mental Health Care: Personalized medicine approaches are being explored for mental health conditions, aiming to identify the most effective treatments based on individual brain chemistry and genetic predispositions.
Challenges of Personalized Medicine:
- Cost of Testing and Treatment: The cost of genetic testing and personalized therapies can be a barrier to access for many patients.
- Data Privacy and Security: The collection and analysis of personal genetic information raise significant concerns about data privacy and security.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of personalized medicine raises ethical questions about genetic discrimination, informed consent, and the potential for social inequities.
2. Digital Health Technologies: Revolutionizing Patient Engagement and Care
Digital health technologies are rapidly transforming the way healthcare is delivered, empowering patients and healthcare providers with new tools and resources. These technologies encompass a wide range of applications, including mobile health apps, wearable devices, telemedicine platforms, and artificial intelligence (AI)-powered diagnostics.
Benefits of Digital Health Technologies:
- Improved Patient Engagement: Digital health tools can enhance patient engagement by providing access to health information, facilitating communication with healthcare providers, and promoting self-management of chronic conditions.
- Enhanced Disease Management: Wearable devices and mobile health apps can track patient health data, providing valuable insights for disease management and early intervention.
- Remote Monitoring and Diagnosis: Telemedicine platforms enable remote monitoring of patients, facilitating timely diagnosis and treatment, especially in underserved areas.
- Streamlined Clinical Trials: Digital health technologies can optimize clinical trial recruitment, data collection, and analysis, accelerating the development of new drugs and therapies.
Examples of Digital Health Technologies in Action:
- Diabetes Management: Mobile health apps can track blood sugar levels, remind patients to take medication, and provide personalized insights and support.
- Mental Health Care: Telemedicine platforms facilitate remote therapy sessions, expanding access to mental health services for patients in rural areas.
- Cardiovascular Disease Monitoring: Wearable devices can track heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs, alerting patients and healthcare providers to potential health risks.
Challenges of Digital Health Technologies:
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of patient health data collected through digital health technologies is a critical concern.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Lack of interoperability between different digital health platforms can hinder data sharing and integration.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in healthcare raises ethical questions about algorithmic bias, transparency, and accountability.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Accelerating Drug Discovery and Development
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the pharmaceutical industry, accelerating drug discovery and development, and enhancing clinical decision-making. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets, identify potential drug targets, predict drug efficacy and safety, and optimize clinical trial design.
Benefits of AI in Drug Discovery and Development:
- Faster and More Efficient Drug Discovery: AI can accelerate drug discovery by identifying promising drug candidates and prioritizing them for further research.
- Improved Drug Safety and Efficacy: AI algorithms can predict drug interactions and adverse events, enhancing drug safety and efficacy.
- Personalized Medicine: AI can analyze patient data to identify individuals who are most likely to benefit from specific treatments, enabling personalized medicine approaches.
- Optimized Clinical Trial Design: AI can optimize clinical trial design, reducing costs and timelines while ensuring robust data collection.
Examples of AI Applications in Drug Discovery and Development:
- Target Identification: AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of biological information to identify potential drug targets.
- Virtual Screening: AI can screen millions of compounds against specific targets, identifying potential drug candidates.
- Drug Repurposing: AI can identify existing drugs that could be repurposed for new indications, accelerating drug development.
- Clinical Trial Design and Optimization: AI can optimize clinical trial design, reducing costs and timelines while ensuring robust data collection.
Challenges of AI in Drug Discovery and Development:
- Data Availability and Quality: AI algorithms require access to large, high-quality datasets for training and validation.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms can perpetuate existing biases in data, potentially leading to unfair or inaccurate predictions.
- Transparency and Explainability: The decision-making processes of AI algorithms can be opaque, raising concerns about transparency and explainability.
4. Biosimilars and Biobetters: Expanding Access to Innovative Therapies
Biosimilars are biological products that are highly similar to existing biologic drugs (often referred to as reference products), offering a cost-effective alternative for patients. Biobetters are biosimilars that have improved characteristics compared to the reference product, such as enhanced efficacy, safety, or pharmacokinetic properties.
Benefits of Biosimilars and Biobetters:
- Increased Access to Biologic Therapies: Biosimilars and biobetters can significantly reduce the cost of biologic therapies, making them more accessible to a wider range of patients.
- Competition and Innovation: The introduction of biosimilars and biobetters fosters competition in the biologics market, driving innovation and potentially leading to the development of even more effective therapies.
- Cost Savings for Healthcare Systems: Biosimilars and biobetters can generate significant cost savings for healthcare systems, allowing them to allocate resources to other critical needs.
Challenges of Biosimilars and Biobetters:
- Regulatory Approval: Biosimilars and biobetters must undergo rigorous regulatory approval processes to ensure their safety and efficacy.
- Patient Acceptance: Some patients may be hesitant to switch from a reference product to a biosimilar or biobetter, even if it is clinically equivalent.
- Intellectual Property Rights: The development and commercialization of biosimilars and biobetters can be complex, involving intellectual property rights and patent issues.
5. Gene Therapy: Targeting the Root of Disease
Gene therapy is a revolutionary approach to treating diseases by directly targeting the genetic basis of the condition. This involves modifying or replacing defective genes with functional ones, potentially offering a cure for a wide range of diseases.
Benefits of Gene Therapy:
- Potential for Cures: Gene therapy has the potential to cure diseases that are currently incurable, such as cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and certain types of cancer.
- Long-Term Benefits: Gene therapy can provide long-lasting or even permanent benefits, reducing the need for ongoing treatment.
- Novel Therapeutic Approaches: Gene therapy offers novel therapeutic approaches for diseases that are difficult to treat with conventional therapies.
Challenges of Gene Therapy:
- Delivery Challenges: Delivering genes to the target cells and tissues can be a significant challenge.
- Safety Concerns: Gene therapy raises safety concerns, such as the potential for unintended gene modifications or immune responses.
- Cost and Access: Gene therapy can be very expensive, making it inaccessible to many patients.
6. Cell Therapy: Regenerating Damaged Tissues
Cell therapy involves using cells to repair or replace damaged tissues, offering a promising approach for treating diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders. This includes using stem cells, immune cells, or other types of cells to regenerate damaged tissues or enhance the body’s natural healing processes.
Benefits of Cell Therapy:
- Regenerative Potential: Cell therapy has the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, offering a new avenue for treating diseases that are currently difficult to manage.
- Immunotherapy: Cell therapy can be used to enhance the body’s immune system, targeting and destroying cancer cells or other disease-causing cells.
- Personalized Treatments: Cell therapy can be tailored to individual patients, using their own cells to create personalized treatments.
Challenges of Cell Therapy:
- Cell Source and Manufacturing: Obtaining and manufacturing the necessary cells for therapy can be challenging and expensive.
- Safety Concerns: Cell therapy raises safety concerns, such as the risk of tumor formation or immune rejection.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of stem cells in cell therapy raises ethical considerations, particularly the use of embryonic stem cells.
7. Data Analytics and Big Data: Driving Insights and Decision-Making
Data analytics and big data are playing an increasingly important role in the pharmaceutical industry, enabling the analysis of vast datasets to identify trends, optimize operations, and improve decision-making. This includes using data analytics to analyze patient data, clinical trial data, market trends, and other relevant information.
Benefits of Data Analytics and Big Data:
- Improved Decision-Making: Data analytics can provide insights into patient populations, disease trends, and market dynamics, improving decision-making across all aspects of the pharmaceutical industry.
- Personalized Medicine: Data analytics can be used to personalize treatments, identify patients who are most likely to benefit from specific therapies, and predict drug response.
- Enhanced Drug Discovery and Development: Data analytics can accelerate drug discovery by identifying promising drug candidates, optimizing clinical trial design, and improving drug safety and efficacy.
Challenges of Data Analytics and Big Data:
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting patient data and ensuring its privacy is paramount in the age of big data.
- Data Integration and Standardization: Integrating and standardizing data from multiple sources can be a significant challenge.
- Data Interpretation and Analysis: Interpreting and analyzing large datasets requires specialized skills and expertise.
8. Regulatory Landscape: Navigating the Changing Environment
The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, with new regulations and guidelines being introduced to address emerging technologies, ensure patient safety, and promote innovation. This includes regulations related to personalized medicine, digital health technologies, gene therapy, cell therapy, and data privacy.
Benefits of Regulatory Landscape Changes:
- Patient Safety: New regulations and guidelines aim to ensure the safety and efficacy of new drugs and therapies, protecting patients from harm.
- Innovation: Regulatory changes can foster innovation by providing clear guidelines for the development and commercialization of new technologies and therapies.
- Transparency and Accountability: Regulatory changes can promote transparency and accountability in the pharmaceutical industry, building trust with patients and healthcare providers.
Challenges of Regulatory Landscape Changes:
- Complexity and Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape can be complex and uncertain, making it difficult for companies to navigate and comply with all regulations.
- Cost and Timelines: Complying with new regulations can be costly and time-consuming, potentially delaying the development and launch of new drugs and therapies.
- Global Harmonization: Harmonizing regulatory requirements across different countries can be challenging, potentially hindering the global development and commercialization of new products.
Related Searches
- Pharmaceutical Industry Trends 2023: Understanding the current trends provides a foundation for anticipating future developments.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Trends 2024: Analyzing the trends for the upcoming year helps stakeholders prepare for upcoming changes and opportunities.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Outlook 2025: This search focuses on providing a comprehensive overview of the industry’s expected trajectory in 2025.
- Future of Pharmaceutical Industry: Exploring the long-term trends and potential advancements shaping the industry’s future.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Innovation: Examining the latest innovations and breakthroughs in drug discovery, development, and delivery.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Challenges: Identifying the key challenges facing the industry, such as rising costs, regulatory hurdles, and competition.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Research: Exploring the ongoing research and development activities shaping the industry’s future.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Market Size: Understanding the global market size and growth potential of the pharmaceutical industry.
FAQs
Q: What are the most significant trends shaping the pharmaceutical industry in 2025?
A: The most significant trends shaping the pharmaceutical industry in 2025 include personalized medicine, digital health technologies, artificial intelligence, biosimilars and biobetters, gene therapy, cell therapy, data analytics and big data, and the evolving regulatory landscape.
Q: How will personalized medicine impact the pharmaceutical industry?
A: Personalized medicine will revolutionize drug development and patient care, enabling the creation of therapies tailored to individual patients’ genetic makeup and disease characteristics. This will lead to more effective treatments, improved patient safety, and potentially lower healthcare costs.
Q: What are the benefits of digital health technologies in the pharmaceutical industry?
A: Digital health technologies offer numerous benefits, including improved patient engagement, enhanced disease management, remote monitoring and diagnosis, and streamlined clinical trials. They can empower patients to take a more active role in their health and improve healthcare delivery.
Q: How is AI transforming drug discovery and development?
A: AI is revolutionizing drug discovery and development by accelerating the identification of potential drug candidates, predicting drug efficacy and safety, and optimizing clinical trial design. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and generate insights that would be impossible for humans to uncover.
Q: What are the challenges associated with gene therapy and cell therapy?
A: Gene therapy and cell therapy face significant challenges, including delivery challenges, safety concerns, and high costs. These challenges need to be addressed before these technologies can be widely adopted.
Q: How can data analytics and big data benefit the pharmaceutical industry?
A: Data analytics and big data can provide valuable insights into patient populations, disease trends, and market dynamics, enabling more informed decision-making across all aspects of the pharmaceutical industry.
Q: What are the implications of the evolving regulatory landscape for the pharmaceutical industry?
A: The evolving regulatory landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for the pharmaceutical industry. New regulations aim to ensure patient safety, promote innovation, and foster transparency and accountability. However, complying with these regulations can be costly and time-consuming.
Tips
- Embrace Digital Transformation: Invest in digital health technologies to enhance patient engagement, improve disease management, and streamline operations.
- Prioritize Personalized Medicine: Develop therapies that are tailored to individual patients’ needs, leveraging advances in genomics and other "omics" technologies.
- Harness the Power of AI: Utilize AI to accelerate drug discovery, optimize clinical trials, and enhance clinical decision-making.
- Explore Biosimilars and Biobetters: Consider developing biosimilars and biobetters to expand access to innovative therapies and reduce healthcare costs.
- Invest in Gene Therapy and Cell Therapy: Explore the potential of gene therapy and cell therapy to develop cures for currently incurable diseases.
- Leverage Data Analytics and Big Data: Utilize data analytics and big data to gain insights into patient populations, disease trends, and market dynamics.
- Stay Informed about Regulatory Changes: Keep abreast of evolving regulatory requirements and ensure compliance with all regulations.
Conclusion
The pharmaceutical industry is at a pivotal juncture, driven by a confluence of transformative trends that are reshaping the landscape of drug discovery, development, and patient care. Personalized medicine, digital health technologies, artificial intelligence, biosimilars and biobetters, gene therapy, cell therapy, data analytics and big data, and the evolving regulatory landscape are all poised to shape the future of the industry. By embracing these trends and navigating the challenges they present, pharmaceutical companies can position themselves for success in the years to come, ultimately driving innovation and improving patient outcomes.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Pharmaceutical Industry Trends 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!