Shaping the Future: Key Trends in the Finance Industry by 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Key Trends in the Finance Industry by 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Key Trends in the Finance Industry by 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Key Trends in the Finance Industry by 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future: Key Trends in the Finance Industry by 2025
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Open Finance
- 3.2 2. The Exponential Growth of Fintech
- 3.3 3. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 3.4 4. The Growing Importance of Data Analytics
- 3.5 5. The Rise of Sustainable Finance
- 3.6 6. The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
- 3.7 7. The Rise of Cloud Computing
- 3.8 8. The Growing Importance of Regulatory Compliance
- 4 Related Searches:
- 5 FAQs:
- 6 Closure
Shaping the Future: Key Trends in the Finance Industry by 2025

The financial landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and evolving regulatory landscapes. As we approach 2025, several trends are poised to reshape the industry, impacting how financial institutions operate, how consumers manage their finances, and how the global economy functions.
1. The Rise of Open Finance
Open finance signifies a paradigm shift in how individuals and businesses access and manage their financial data. It envisions a future where consumers have greater control over their financial information, allowing them to share it securely with various applications and services. This empowers consumers to make more informed financial decisions, access personalized financial products, and potentially unlock new opportunities for wealth creation.
How Open Finance is Transforming the Industry:
- Enhanced Financial Control: Consumers can consolidate their financial data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive view of their finances. This enables better budgeting, debt management, and investment decisions.
- Personalized Financial Products: Financial institutions can leverage shared data to offer customized products and services tailored to individual needs and risk profiles.
- Emergence of Fintech Innovation: Open finance fosters the development of innovative fintech applications, offering a wider range of financial solutions beyond traditional banking.
- Improved Financial Inclusion: By lowering barriers to entry, open finance can empower individuals and businesses in underserved communities to access financial services.
Examples of Open Finance Applications:
- Financial Aggregators: Platforms like Plaid and Yodlee allow users to connect their bank accounts and other financial accounts, providing a centralized view of their finances.
- Personalized Financial Advice: Robo-advisors and financial planning tools leverage open finance data to offer tailored investment recommendations.
- Automated Bill Payments: Open finance enables seamless integration with bill payment services, simplifying financial management.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring the secure handling of sensitive financial data is paramount. Robust security measures and clear data privacy regulations are crucial.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Establishing standardized protocols and APIs is essential for seamless data sharing between different financial institutions and applications.
- Consumer Education and Awareness: Raising consumer awareness about open finance benefits and potential risks is vital to promote responsible adoption.
2. The Exponential Growth of Fintech
Fintech encompasses the use of technology to improve and automate financial services. This trend is rapidly accelerating, fueled by the increasing adoption of mobile devices, the rise of big data analytics, and the demand for more accessible and affordable financial solutions.
Key Areas of Fintech Innovation:
- Digital Banking: Neobanks and challenger banks are disrupting traditional banking models by offering mobile-first experiences, simplified account opening, and competitive fees.
- Payments and Transfers: Mobile payment solutions like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Venmo are becoming increasingly popular, offering convenience and security for transactions.
- Lending and Credit: Fintech companies are leveraging alternative data sources and machine learning to assess creditworthiness and offer personalized loan products.
- Investment Management: Robo-advisors and algorithmic trading platforms are making investment management accessible to a wider audience, offering automated portfolio management and low fees.
- Insurance: Insurtech companies are using technology to streamline insurance processes, personalize policies, and offer innovative products.
Impact of Fintech on the Finance Industry:
- Increased Competition: Fintech companies are challenging traditional financial institutions, forcing them to adapt and innovate to remain competitive.
- Improved Customer Experience: Fintech solutions often offer more convenient and personalized experiences than traditional financial services.
- Enhanced Financial Inclusion: Fintech can provide access to financial services for underserved populations, including those in rural areas and low-income households.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Regulation and Compliance: The rapid growth of fintech necessitates clear regulatory frameworks to ensure consumer protection and financial stability.
- Data Security and Privacy: Fintech companies must prioritize data security and privacy to protect customer information from cyber threats.
- Talent Acquisition: The fintech industry requires skilled professionals with expertise in technology, finance, and data analytics.
3. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming the finance industry by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and creating personalized customer experiences. These technologies are being applied across various areas, including:
Applications of AI and ML in Finance:
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of transaction data to identify suspicious patterns and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Risk Management: ML models can assess credit risk, market risk, and operational risk, enabling financial institutions to make more informed decisions.
- Personalized Financial Advice: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide personalized financial advice and support to customers.
- Algorithmic Trading: AI algorithms can execute trades based on pre-defined parameters, potentially improving investment returns.
- Customer Service Automation: AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Impact of AI and ML on the Finance Industry:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI and ML can automate repetitive tasks, allowing financial institutions to operate more efficiently and allocate resources to higher-value activities.
- Improved Decision-Making: AI and ML can analyze data to identify patterns and insights that may not be apparent to humans, leading to better-informed decisions.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: AI-powered tools can provide personalized financial advice, support, and services, creating a more seamless customer experience.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Explainability and Transparency: Understanding how AI and ML algorithms make decisions is crucial for trust and accountability.
- Data Bias: AI models can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Job Displacement: The automation of tasks by AI and ML could lead to job displacement in some areas of the finance industry.
4. The Growing Importance of Data Analytics
Data analytics is becoming increasingly critical for financial institutions to make informed decisions, manage risk, and improve customer service. The ability to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including customer transactions, market trends, and regulatory filings, provides valuable insights that can drive growth and efficiency.
Applications of Data Analytics in Finance:
- Customer Segmentation: Data analytics can be used to segment customers into different groups based on their demographics, behavior, and financial needs. This allows financial institutions to tailor products and services to specific customer segments.
- Market Research: Data analytics can help financial institutions understand market trends, identify investment opportunities, and develop new products and services.
- Risk Assessment: Data analytics can be used to assess credit risk, market risk, and operational risk, enabling financial institutions to make more informed decisions about lending, investing, and managing their operations.
- Fraud Detection: Data analytics can be used to identify suspicious patterns in transactions and prevent fraudulent activities.
Impact of Data Analytics on the Finance Industry:
- Improved Decision-Making: Data analytics provides financial institutions with a deeper understanding of their customers, markets, and risks, enabling them to make more informed decisions.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Data analytics can be used to personalize customer interactions and provide more relevant products and services.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Data analytics can help financial institutions identify areas where they can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Data Quality and Integrity: Ensuring the quality and integrity of data is essential for accurate analysis and informed decision-making.
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount. Financial institutions must implement robust data security measures and comply with data privacy regulations.
- Talent Acquisition: The finance industry needs skilled data scientists and analysts to leverage the power of data analytics.
5. The Rise of Sustainable Finance
Sustainable finance encompasses financial activities that consider environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Investors are increasingly demanding that their investments align with their values and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Key Trends in Sustainable Finance:
- ESG Investing: Investors are incorporating ESG factors into their investment decisions, seeking companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices.
- Green Bonds: Bonds issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure, are becoming increasingly popular.
- Impact Investing: Investing in companies or projects that aim to generate positive social or environmental impact alongside financial returns.
- Sustainable Banking: Financial institutions are developing products and services that promote sustainable practices, such as green mortgages and loans for renewable energy projects.
Impact of Sustainable Finance on the Finance Industry:
- Shifting Investment Preferences: Investors are increasingly allocating capital to sustainable investments, driving demand for ESG-compliant products and services.
- Increased Regulatory Focus: Governments and regulators are introducing policies and regulations to promote sustainable finance, including mandatory ESG reporting requirements.
- Innovation and Opportunity: Sustainable finance is creating new opportunities for financial institutions to develop innovative products and services that address environmental and social challenges.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Data Measurement and Reporting: Developing standardized metrics and reporting frameworks for ESG factors is crucial for accurate assessment and comparison.
- Integration with Existing Investment Practices: Integrating ESG considerations into traditional investment practices requires a significant shift in mindset and processes.
- Consumer Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about sustainable finance and the benefits of investing in ESG-compliant products is essential for driving adoption.
6. The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has become a paramount concern for financial institutions, as they face increasing threats from cyberattacks. Protecting sensitive customer data, financial systems, and critical infrastructure is essential to maintain trust and ensure operational stability.
Key Cybersecurity Challenges for Financial Institutions:
- Sophisticated Cyberattacks: Cybercriminals are employing increasingly sophisticated techniques, including ransomware, phishing scams, and data breaches, to target financial institutions.
- Data Breaches: The theft of sensitive customer data can have devastating consequences, including reputational damage, financial losses, and legal liabilities.
- Compliance with Regulations: Financial institutions must comply with evolving cybersecurity regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Cybersecurity Solutions for Financial Institutions:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords, biometrics, and one-time codes, can significantly enhance security.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit protects it from unauthorized access.
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response: Continuously monitoring for suspicious activity and responding quickly to security incidents is essential to mitigate damage.
- Employee Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices is crucial to prevent human error and social engineering attacks.
Impact of Cybersecurity on the Finance Industry:
- Increased Investment in Security: Financial institutions are investing heavily in cybersecurity technologies, personnel, and training to strengthen their defenses.
- Enhanced Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulators are increasing their scrutiny of financial institutions’ cybersecurity practices, imposing stricter compliance requirements.
- Shifting Security Focus: Financial institutions are shifting their focus from perimeter security to a more comprehensive approach that encompasses all aspects of their operations, including cloud computing, mobile devices, and third-party vendors.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Talent Shortage: The cybersecurity industry faces a severe shortage of skilled professionals, making it challenging for financial institutions to find and retain qualified talent.
- Evolving Threat Landscape: Cybercriminals are constantly developing new attack methods, requiring financial institutions to stay ahead of the curve and adapt their security strategies.
- Balancing Security with User Experience: Financial institutions must strike a balance between security measures and the user experience, ensuring that security protocols do not hinder customer convenience.
7. The Rise of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is transforming the finance industry by providing flexible, scalable, and cost-effective computing resources. Financial institutions are increasingly adopting cloud-based solutions to manage their operations, store data, and deliver services.
Benefits of Cloud Computing for Financial Institutions:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing allows financial institutions to scale their resources up or down as needed, meeting fluctuating demand and reducing costs.
- Cost Savings: Cloud computing can reduce the need for expensive hardware and IT infrastructure, leading to significant cost savings.
- Improved Security: Cloud providers offer robust security measures and compliance certifications, helping financial institutions protect sensitive data.
- Faster Innovation: Cloud computing enables faster development and deployment of new applications and services, allowing financial institutions to respond quickly to market changes.
Applications of Cloud Computing in Finance:
- Digital Banking: Cloud-based platforms power mobile banking apps, online banking services, and other digital banking solutions.
- Data Analytics: Cloud computing provides the infrastructure and processing power needed for large-scale data analysis.
- Risk Management: Cloud-based risk management solutions help financial institutions manage credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Cloud-based CRM systems enable financial institutions to manage customer relationships, track interactions, and provide personalized services.
Impact of Cloud Computing on the Finance Industry:
- Increased Adoption of Digital Services: Cloud computing is driving the adoption of digital banking, mobile payments, and other online financial services.
- Enhanced Innovation: Cloud computing allows financial institutions to experiment with new technologies and develop innovative products and services more quickly.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Cloud computing streamlines operations, reduces IT costs, and frees up employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of data stored in the cloud is paramount. Financial institutions must carefully choose cloud providers with robust security measures and comply with data privacy regulations.
- Vendor Lock-In: Financial institutions must be aware of the potential for vendor lock-in, ensuring that they can easily migrate their data and applications to other cloud providers if needed.
- Talent Acquisition: Financial institutions need skilled cloud computing professionals to manage and maintain their cloud infrastructure and applications.
8. The Growing Importance of Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance remains a critical aspect of the finance industry, ensuring that financial institutions operate within the legal and ethical frameworks governing their activities. The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, requiring financial institutions to stay informed about new regulations and adapt their practices accordingly.
Key Regulatory Trends in the Finance Industry:
- Increased Scrutiny of ESG Factors: Regulators are increasingly focusing on ESG factors, requiring companies to disclose their environmental, social, and governance practices.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Data privacy regulations, such as the GDPR and the CCPA, are becoming more stringent, requiring financial institutions to protect sensitive customer data.
- Cybersecurity Regulations: Regulations such as the New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) Cybersecurity Regulation are imposing stricter cybersecurity requirements on financial institutions.
- Financial Inclusion Initiatives: Regulators are promoting financial inclusion initiatives, aiming to provide access to financial services for underserved populations.
Impact of Regulatory Compliance on the Finance Industry:
- Increased Compliance Costs: Meeting regulatory requirements can be costly for financial institutions, requiring investments in technology, personnel, and training.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Compliance with regulations helps financial institutions manage risk and protect themselves from legal liabilities.
- Improved Customer Trust: Compliance with regulations demonstrates to customers that financial institutions are operating ethically and responsibly.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Keeping Up with Evolving Regulations: The regulatory landscape is constantly changing, requiring financial institutions to stay informed about new regulations and adapt their practices accordingly.
- Balancing Compliance with Innovation: Financial institutions must find ways to comply with regulations while also fostering innovation and developing new products and services.
- Building a Culture of Compliance: A strong culture of compliance is essential to ensure that all employees understand and adhere to regulatory requirements.
Related Searches:
1. Future of Finance:
The future of finance is being shaped by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and evolving regulatory landscapes. The trends discussed above are just a glimpse into the transformative changes that are taking place.
2. Finance Industry Trends 2024:
The trends identified for 2025 are already gaining momentum in 2024, with financial institutions actively adapting to these changes. Expect to see further adoption of open finance, fintech innovation, AI and ML applications, and a growing emphasis on data analytics, sustainable finance, cybersecurity, cloud computing, and regulatory compliance.
3. Financial Technology Trends:
Fintech is at the forefront of innovation in the finance industry. The trends discussed above highlight the key areas of fintech development, including digital banking, payments and transfers, lending and credit, investment management, and insurance.
4. Digital Banking Trends:
Digital banking is rapidly transforming how consumers manage their finances. Neobanks and challenger banks are disrupting traditional banking models by offering mobile-first experiences, simplified account opening, and competitive fees.
5. AI in Finance:
AI is being applied across various areas of finance, from fraud detection and risk management to personalized financial advice and algorithmic trading. The adoption of AI is expected to accelerate in the coming years, leading to further automation, improved decision-making, and enhanced customer experiences.
6. Blockchain in Finance:
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing finance by enabling secure, transparent, and efficient transactions. Applications include cryptocurrency trading, digital asset management, and supply chain finance.
7. Sustainable Finance Trends:
Sustainable finance is gaining momentum, with investors increasingly demanding that their investments align with their values and contribute to a more sustainable future. ESG investing, green bonds, impact investing, and sustainable banking are key trends in this area.
8. Fintech Regulation:
As fintech continues to grow, regulators are working to establish clear frameworks to ensure consumer protection, financial stability, and fair competition. The regulatory landscape for fintech is evolving rapidly, requiring financial institutions and fintech companies to stay informed about new rules and regulations.
FAQs:
1. What are the biggest challenges facing the finance industry in the next few years?
The finance industry faces a number of significant challenges, including:
- Cybersecurity threats: The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks poses a major risk to financial institutions.
- Regulatory compliance: The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, requiring financial institutions to stay informed about new rules and regulations.
- Competition from fintech: Fintech companies are disrupting traditional financial institutions, forcing them to innovate and adapt to remain competitive.
- Talent acquisition: The finance industry needs skilled professionals with expertise in technology, finance, and data analytics.
- Data privacy and security: Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount, requiring financial institutions to implement robust security measures and comply with data privacy regulations.
2. How can financial institutions prepare for the future?
To prepare for the future, financial institutions should:
- Embrace technology: Adopt new technologies, such as AI, ML, cloud computing, and blockchain, to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and develop innovative products and services.
- **

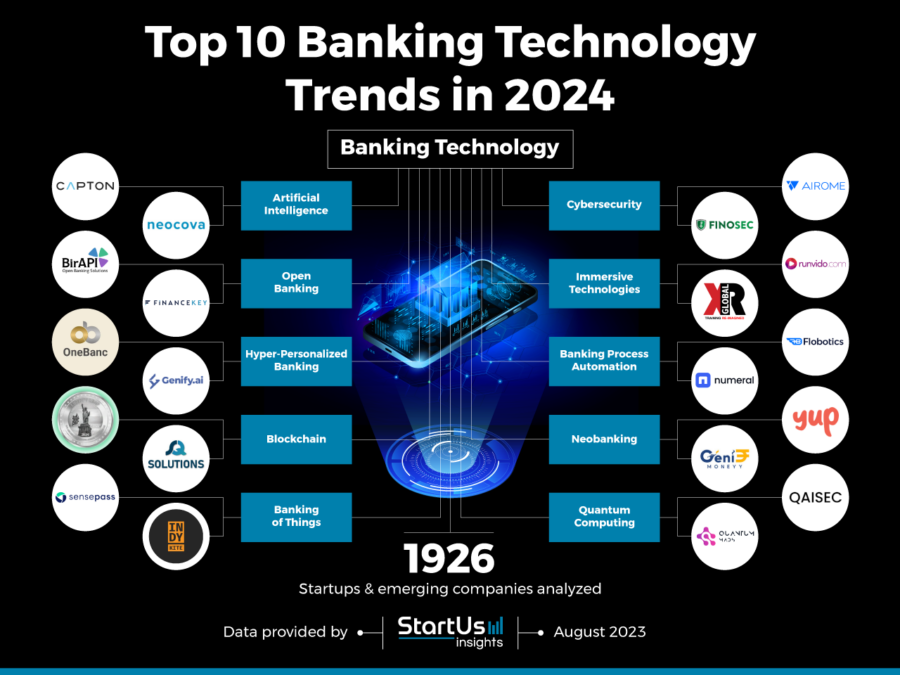
![The Future of Finance [Infographic]](https://infographicjournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/The-Future-of-Finance-feat.png)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Key Trends in the Finance Industry by 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!